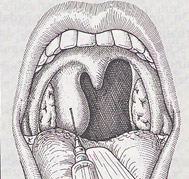
 The oral cavity is located below the nasal passages and is the initial part of the digestive tract.
The oral cavity is located below the nasal passages and is the initial part of the digestive tract.
There are two distinct zones composed, separated by the upper and lower dental arches:
- the vestibule in front, bounded on the sides by the cheeks and in front by the lips,
- and oral cavity, further back, between the teeth in front, and the pillars of the soft palate, back.
The mouth has three essential components:
– teeth, of which only the crown is visible at the opening of the mouth, are located on the edge of maxilla;
– tongue, set in the posterior and mobile for the rest, thanks to the work of seventeen small muscles that allow swallowing and phonation. Buds that cover its surface are receptors of taste;
– and salivary glands, three in number on each side:
— parotid glands,
— the submandibular glands,
— and sublingual glands.
The mouth has several roles:
– Mechanical:
— ingestion of food by chewing teeth grinding, moistening with saliva,
— transport / swallowing the food bolus through the action of the tongue and pharyngeal muscles, is directed into the esophagus.
– Chemical: beginning of the breakdown of sugars by an enzyme in saliva. The excretory ducts of salivary glands open at the floor of the mouth. The enzymes in saliva help a pre-digestion of food all the more important as chewing is extended.
– Convective (breathing): The oral cavity also allows the passage of air from the outside to the pharynx, then to the larynx.
– Phonation: The position, movements and contractions of the language spoken to the issue of sound.
– The taste: is the body language of taste receptors, being the lingual papillae.
Oral pathology is dominated by infections (mycoses) and irritation (frottments, mouth ulcers ..), but also by the tumor pathology.
 Italiano
Italiano
 English
English
 Français
Français
 Русский
Русский
 Română
Română